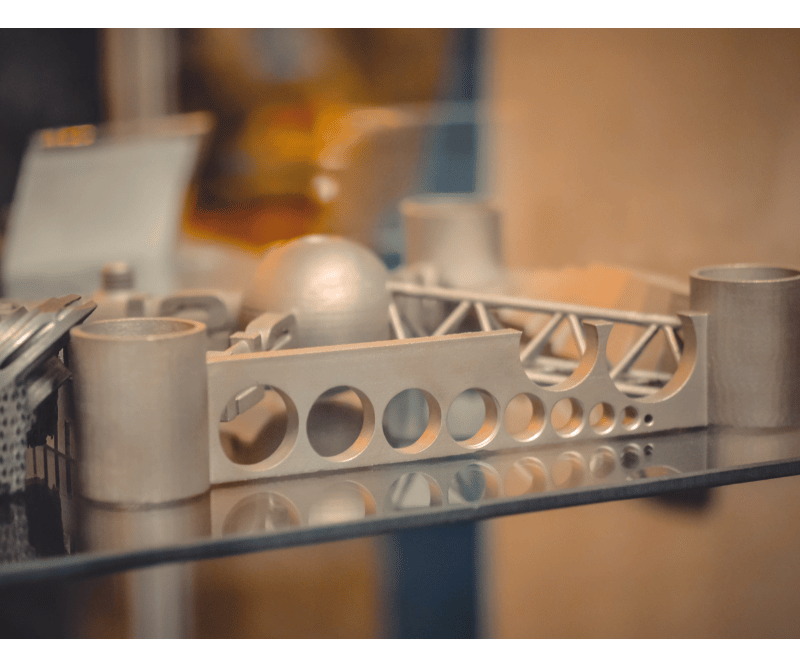
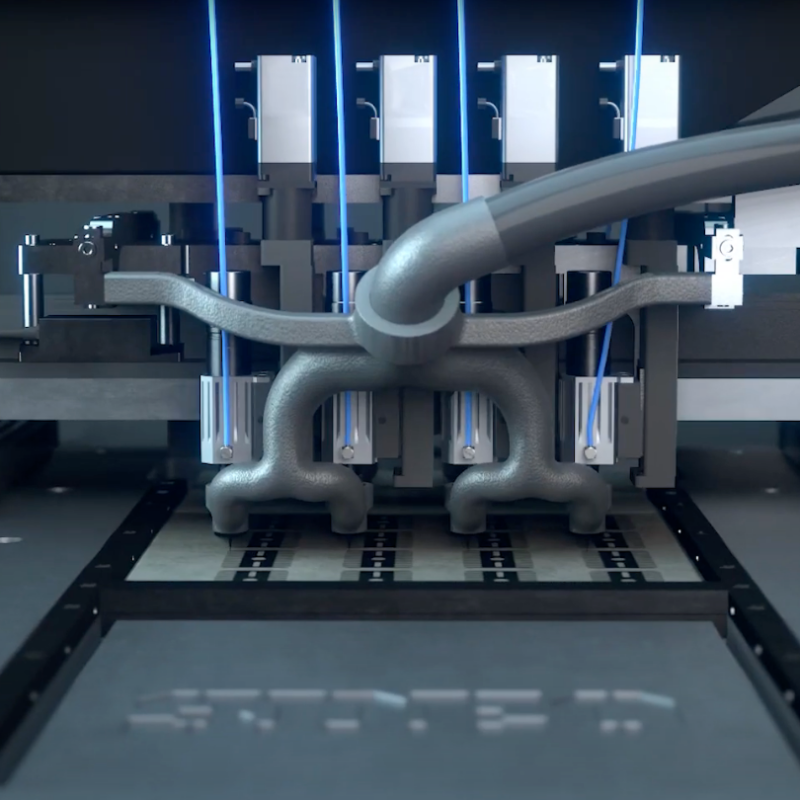
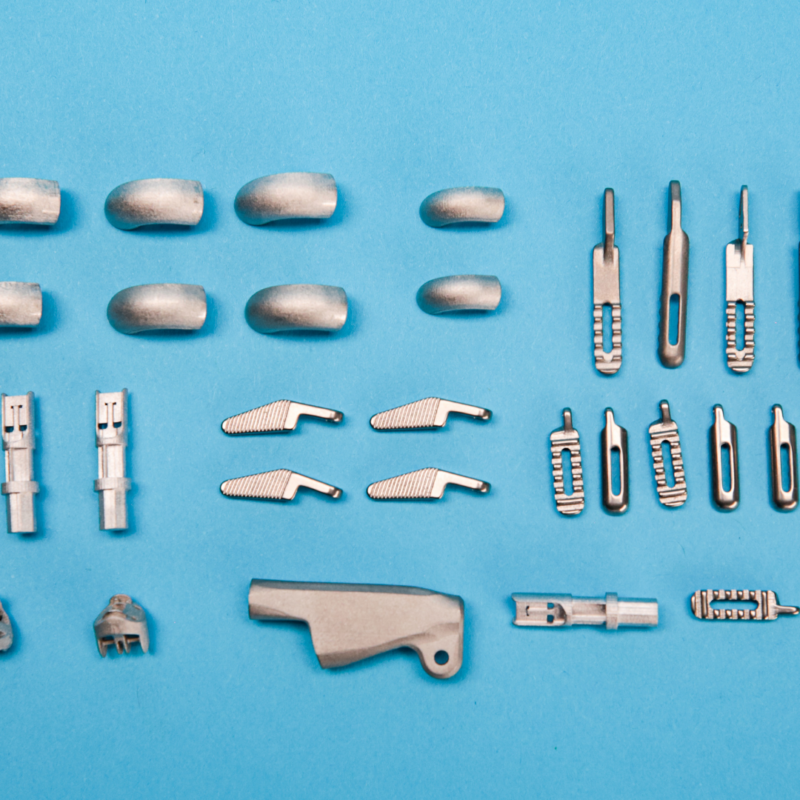
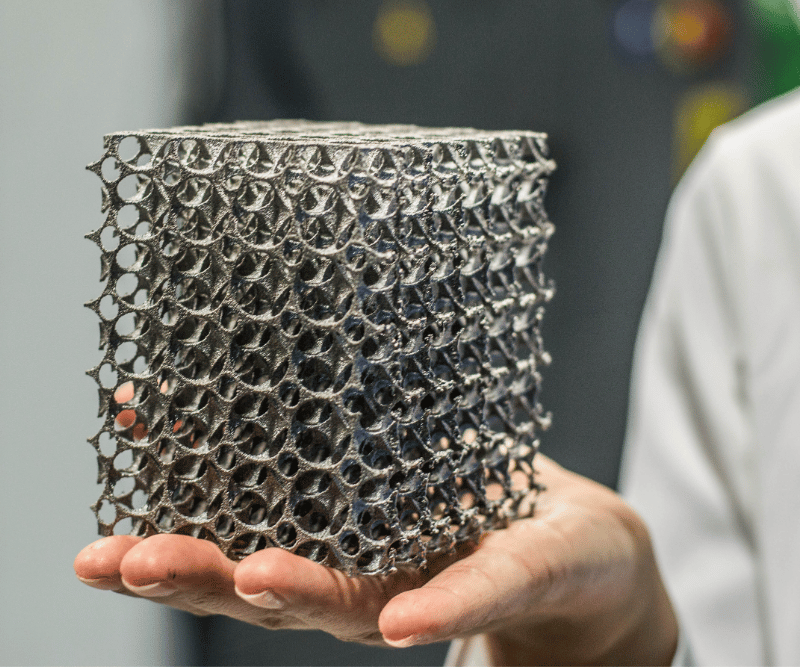
How does 3D metal printing work? By understanding the inner workings of 3D metal printing, you can appreciate the complexity and realize the potential of this revolutionary manufacturing technique.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative applications and possibilities in the future. This article will explore the common 3D metal printing processes found in many firms, including ones found at 3DEO.
3DEO’s 3D metal printing technology and process is unique in that it was designed to compete with traditional manufacturing processes compared to many other types of 3D metal printing.
Key Takeaways
- The design process involves creating a digital design and converting it into a format understood by the 3D metal printer.
- The printing process involves depositing metal powder onto a build platform and selectively melting and fusing the powder layers together.
- Post-processing techniques such as heat treatment, machining, and surface coating are used to improve strength, surface finish, and dimensional accuracy of the printed object.
- 3D metal printing offers advantages such as the ability to produce complex designs, cost savings, enhanced customization, and improved functionality in various industries.
- 3DEO, in particular, offers distinct advantages through our Intelligent Layering® 3D metal printing technology such as the flexibility of 3D printing while also improving scalability that rivals traditional manufacturing processes
Understanding the Basics of 3D Metal Printing
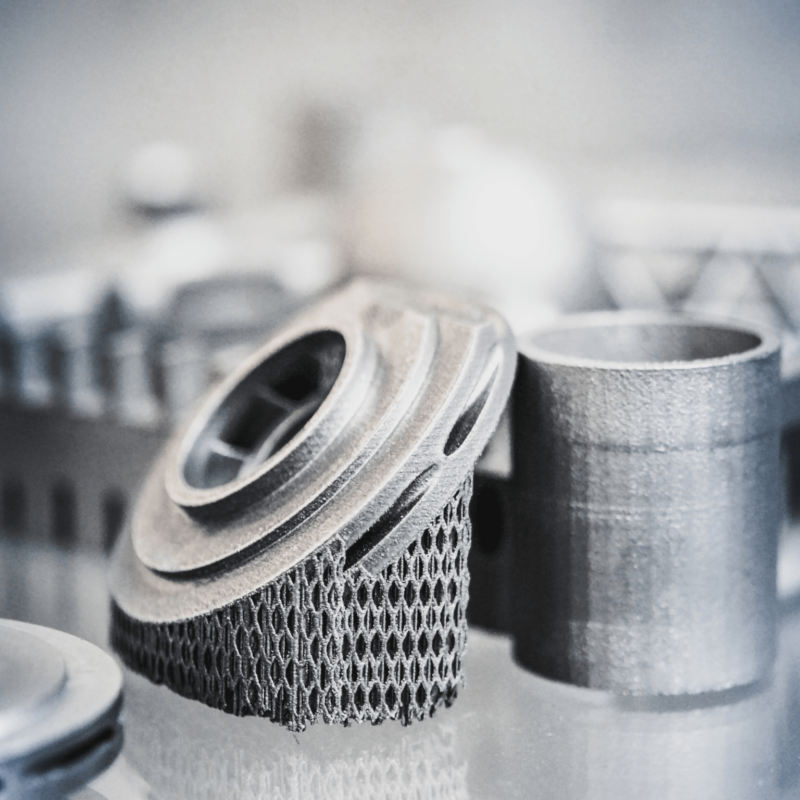
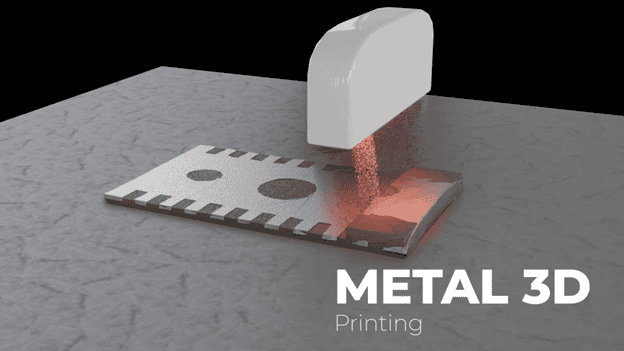
3D metal printing allows you to create three-dimensional objects by layering metal powder and fusing it together using a powerful laser.
One of the major advantages of 3D metal printing is the ability to produce complex and intricate designs that would be impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. Additionally, this manufacturing process offers significant cost savings as it eliminates the need for expensive molds or tooling.
On the other hand, there are also some disadvantages to consider. The cost of metal powders and the initial investment in a 3D metal printer can be high. Scalability can pose a challenge as some printing processes can be time-consuming, especially for large-scale production.
The Design Process in 3D Metal Printing
In the world of 3D metal printing, the design optimization stage plays a vital role in achieving the desired end result. During this stage, the design is carefully analyzed and modified to ensure it can be successfully printed using metal Additive Manufacturing techniques.
Designers must take into consideration the unique challenges and limitations of 3D metal printing, such as the need for support structures, heat management, and material properties. They also need to consider factors like print orientation and build time optimization.
By iteratively refining the design and making adjustments based on these considerations, designers can create intricate and complex metal parts that meet the desired specifications while minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency.
Material Selection and Preparation
The key to achieving optimal results in 3D metal printing lies in carefully selecting and preparing the right materials.
Material properties play a crucial role in determining the quality and durability of the final product. When it comes to metal printing, metal powder is the primary material used. The choice of metal powder depends on various factors like the desired mechanical properties, such as strength or flexibility, and the intended application of the printed object.
Different metals have different melting points, which affect the printing process. It is essential to select a metal powder that can be easily melted and solidified during the printing process.
Additionally, the metal powder must be carefully prepared to ensure its purity and uniformity, as any impurities can negatively impact the print quality.
The Printing Process: Layer by Layer
In 3D metal printing, layers upon layers of metal powder are meticulously fused together to create a solid, intricately designed object. This is achieved through advanced printing techniques known as Additive Manufacturing.
In the printing process, a thin layer of metal powder is spread across the printing bed. Then, a high-powered laser selectively melts and fuses the powder particles together, forming a solid layer. This process is repeated layer by layer until the desired object is fully formed.
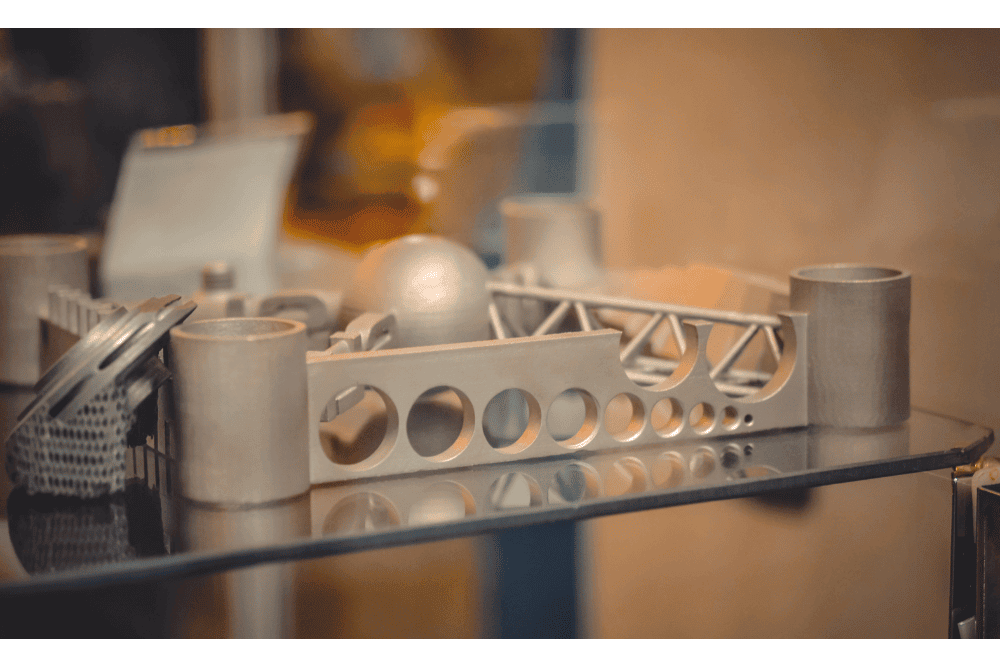
The precision and accuracy of 3D metal printing allow for the creation of complex geometries and intricate designs that would be impossible to achieve through traditional manufacturing methods. Additive Manufacturing revolutionizes the production of metal parts, offering enhanced customization, reduced waste, and increased efficiency in various industries.
Post-Processing and Finishing Techniques
Post-processing and finishing techniques add the final touches to your 3D printed metal masterpiece, giving it a polished, professional look that will leave you in awe.
Surface treatment plays a crucial role in enhancing the appearance and functionality of your creation. Techniques like sanding, polishing, and bead blasting can achieve a smooth and flawless surface, eliminating any imperfections left by the printing process.
Quality control is also a key part of post-processing. Techniques like dimensional accuracy checks and material testing ensure that your 3D printed metal parts meet the highest standards. These checks guarantee that your creation is not only visually appealing but also structurally sound.
Applications and Future Possibilities of 3D Metal Printing
Imagine the endless possibilities of what you can create with 3D metal printing, from intricate jewelry designs to complex aerospace parts, as this technology continues to push the boundaries of innovation.
One of the most exciting aspects of 3D metal printing is its ability to work with advanced metal alloys. This opens up a whole new world of opportunities for creating stronger and more durable products.
For example, in the medical field, 3D metal printing has been used to create prosthetics with customized designs and improved functionality. This technology allows for precise and accurate fabrication, resulting in prosthetics that fit better and provide enhanced comfort and mobility for the wearer.
With further advancements, the future possibilities of 3D metal printing are truly limitless, and we can expect to see even more groundbreaking applications in a growing variety of industries.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the advantages of using 3D metal printing over traditional manufacturing methods?
The advantages of using 3D metal printing over traditional manufacturing methods include greater design flexibility, reduced material waste, faster production times, and the ability to create complex geometries. However, there are limitations in terms of size and cost.
Can 3D metal printing be used for large-scale production or is it mainly limited to prototyping and small-batch production?
It depends on the provider. At 3DEO, 3D metal printing can be used for large-scale production. It is not limited to just prototyping and small-batch production. Additive manufacturing allows for efficient and cost-effective production of complex geometries on a larger scale.
Is 3DEO’s Intelligent Layering® process considered metal 3D printing?
Yes, 3DEO’s Intelligent Layering® is an innovative form of metal 3D printing that combines the best of both CNC manufacturing and metal 3D printing to allow for faster product launches and innovation.
How does the cost of 3D metal printing compare to traditional manufacturing methods?
At 3DEO, cost comparison between 3D metal printing and traditional manufacturing methods can be similar and it depends on factors such as material selection and production volume. By considering these factors, you can determine which method is more cost-effective for your specific needs.